

Next: Local power model
Up: RTL Interconnect Power Estimation
Previous: RTL Interconnect Power Estimation
Several factors decide the power consumed by wires transferring
data between DPUs, the switching activity of the data series
transferred, the wire layout, and the capacitive parameters. We
profile switching activity by simulation using typical input
traces. Then, we use a global wire power model and a local wire
power model to get wire power consumption. The global model
estimates how the wire is routed, its length, and how it is
assigned to different metal layers if multiple metal layers are
used. The local model estimates the unit-length switched
capacitance (the equivalent capacitance due to switching activity
in a unit-length wire) based on the switching activity and
specific metal layer wire capacitive parameters. These two models
together estimates power consumed by the entire data transfer wire
based on the relative positions of the source and the destination,
which are given by an RTL flooplanner. The data transfer wire
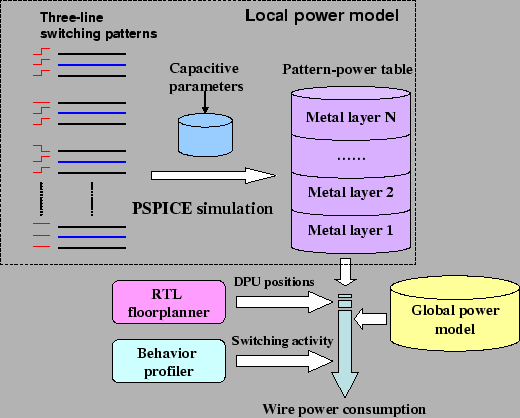
power estimation flow is shown in Fig. 6. Local and
global power models are interconnect power modelling problems
orthogonal to interconnect optimization. In this work, we assume
straightforward ones for both of them, although more sophisticated
models are proposed in a recent work from our group [].
Figure 6:
Local and global wire models, a behavior profiler, and an
RTL floorplanner are used to estimate data transfer wire power
consumption.
 |
Subsections


Next: Local power model
Up: RTL Interconnect Power Estimation
Previous: RTL Interconnect Power Estimation
Lin Zhong
2003-10-11

